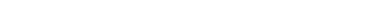Hazard Class

CLASS 1- EXPLOSIVES
Division 1.1 Substances and articles which have a mass explosion hazard
Division 1.2 Substances and articles which have a projection hazard but not a mass explosion hazard
Division 1.3 Substances and articles which have a fire hazard and either a minor blast hazard or a minor projection hazard or both
Division 1.4 Substances and articles which present no significant hazard; only a small hazard in the event of ignition or initiation during transport with any effects largely confined to the package
Division 1.5 Very insensitive substances which have a mass explosion hazard
Division 1.6 Extremely insensitive articles which do not have a mass explosion hazard
Class 2- Gases
Division 2.1 Flammable gas – gases which ignite on contact with an ignition source example acetylene, hydrogen.
Division 2.2 Non flammable gases – gases which are neither flammable nor poisonous example oxygen, nitrogen, neon.
Division 2.3 Poisonous gases – gases liable to cause death or serious injury to human health if inhaled example fluorine, chlorine, hydrogen cyanide.
Class 3- Flammable liquids
Flammable liquids are defined by dangerous goods regulations as liquids, mixtures of liquids or liquids containing solids in solution or suspension which give off a flammable vapour (have a flash point) at temperatures of not more than 60-65°C, liquids offered for transport at temperatures at or above their flash point or substances transported at elevated temperatures in a liquid state and which give off a flammable vapour at a temperature at or below the maximum transport temperature.
Sub-Divisions
There are no subdivisions within Class 3, Flammable Liquids.
Class 4- Flammable solids
Division 4.1 Flammable solids which are easily ignited and readily combustible example nitrocellulose, magnesium, safety or strike-anywhere matches.
Division 4.2 Spontaneously combustible substances example aluminium alkyls, white phosphorus.
Division 4.3 Substances which emit a flammable gas when wet or react violently with water example sodium, calcium, potassium.
CLASS 5- OXIDIZING SUBSTANCES; ORGANIC PEROXIDES
Division 5.1 Oxidising agents other than organic peroxides example calcium hypochlorite, ammonium nitrate , hydrogen peroxide.
Division 5.2 Organic peroxides ,either in liquid or solid form example benzoyl peroxides, cumene hydroperoxide.
Class 6- Poisonous toxic and infectious substances
Division 6.1 Poisonous substances which are liable to cause death or serious injury to human health if inhaled, swallowed or by skin absorption example potassium cyanide, mercuric chloride, hydrofluoric acid.
Division 6.2 Biohazardous substances example virus cultures, pathology specimens, used intravenous needles.
CLASS 7- RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL
Dangerous goods regulations define radioactive material as any material containing radionuclides where both the activity concentration and the total activity exceeds certain pre-defined values. A radionuclide is an atom with an unstable nucleus and which consequently is subject to radioactive decay.
Sub-Divisions
There are no subdivisions within Class 7, Radioactive Material.
CLASS 8- CORROSIVES
Corrosives are substances which by chemical action degrade or disintegrate other materials upon contact.
Sub-Divisions
There are no subdivisions within Class 8, Corrosives.
CLASS 9 – MISCELLANEOUS DANGEROUS GOODS
Miscellaneous dangerous goods are substances and articles which during transport present a danger or hazard not covered by other classes. This class encompasses, but is not limited to, environmentally hazardous substances, substances that are transported at elevated temperatures, miscellaneous articles and substances, genetically modified organisms and micro-organisms and (depending on the method of transport) magnetized materials and aviation regulated substances.
Sub-Divisions
There are no subdivisions within Class 9, Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods.
DG Sea Freight

We have always been focusing on dangerous goods transportation by sea!
1.Why choose us?
Professional&Efficient Carriers
We have established deep partnerships with major shipping companies around the world, such as MAERSK, MSC, CMA, HPL... And organise pick-up and delivery by specialised carriers, arrange special packaging and labelling of hazardous cargo and prepare all necessary documentation according to international rules and regulations.
Experienced and reliable Team
We growing up with the ever-changing market, and keep learning and mastering the new applicable regulations on global forwarding of hazardous cargo. We have specialized team who are trained and certified in the handling of hazardous cargo by sea, air and by road. This enables us to provide you with the complete supply chain service. And ensures that your shipment is carried properly and securely.
According to each customer's different needs, we provide a full range of service and tailored solutions. And our professional team is always on your side.
2. Dangerous goods operated by ROCHA:
Class 2 Gas & Aerosols, such as air fresheners, refrigerants, carbon dioxide gas...
Class 3 Paints, Resins, Lubricants...
Class 4 Yellow Phosphorus, Aluminum Powder...
Class 5 Hydrogen peroxide, bleach powder...
Class 6 Aniline, TDI, Arsenic...
Class 7 Krypton-85 balance inert gas
Class 8 Sulfuric Acid, Nitric Acid, Phosphoric Acid...
Class 9 Dry Ice, Lithium Battery...
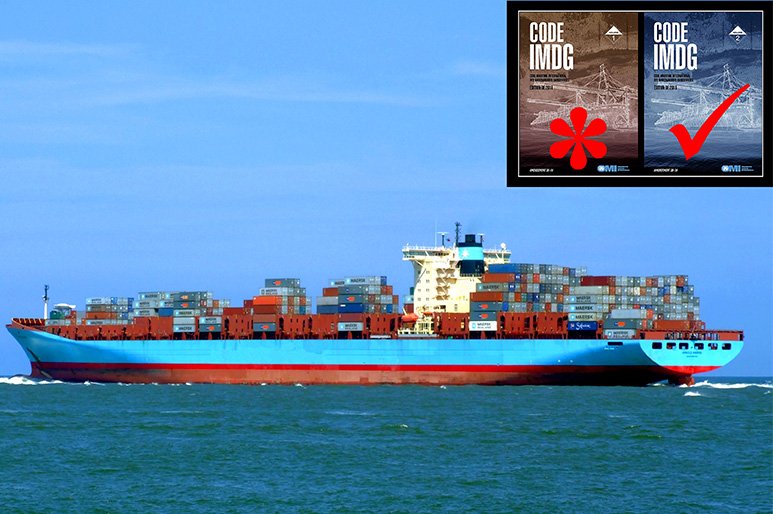
DG Air Freight

We mainly handle dangerous goods air transporation in Hong Kong. Hong Kong as an international airport, means that we have more choices on the flight. And also guarantee on efficiency. We have experienced oprator team to deal with all kinds of dangerous goods in Hong Kong. And established a long-term business relationship with several Airlines(EK,TG,AY,TK,CA...) in dangerous goods air transport area. Usually, we accept most of the chemical products(except radioactive/explosive/compressed gas). Such as biological medicine, pesticides and biological reagents, we can issue relevant certificate, in order to arrange flights for your goods accordingly. Fast, safe, efficient is our goal. To provide you convenience, low cost hazardous air freight service is our mssion!
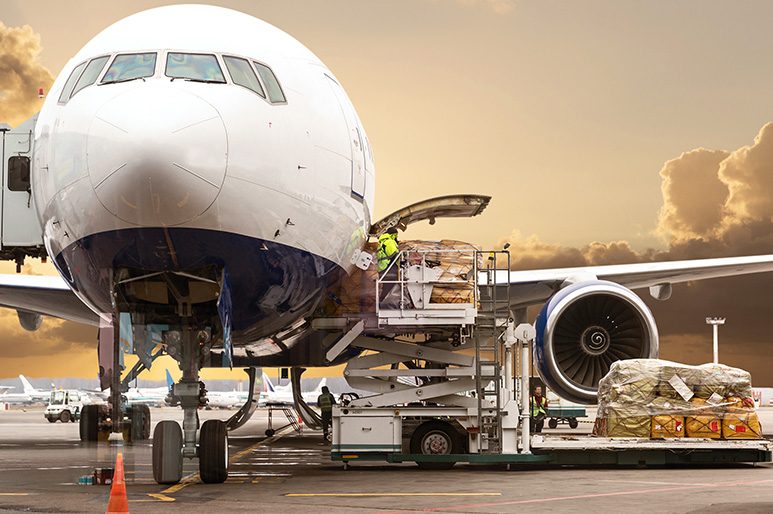
DG Truck Service

We provide dangerous goods trailer services (containers and ISO TANK) at terminals in Shenzhen, Guangzhou and Hong Kong. The scope of carriage is as follows:
The
Class 2 compressed gas and liquefied gas;
Class 3 Flammable liquid
Class 4 flammable solids, pyrophoric articles and wet flammable articles;
Class 5 oxidants and organic peroxides;
Class 6 poisons and infectious articles;
Class 8 corrosion products;
DG Warehouse
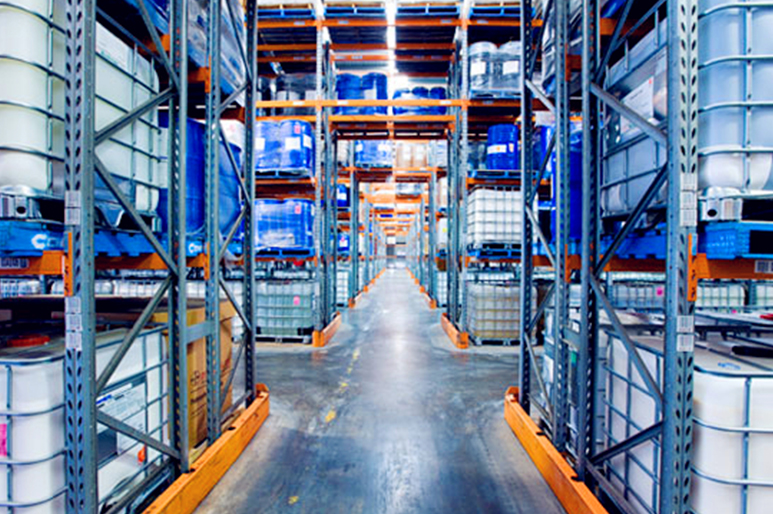

For dangerous goods storage requirments, we can provide professional hazardous warehouse to cooperate with your business. The service including pallet storage, bulk storage, packaging and bundled processing. We have professional hazardous storage management staff to take care of your goods 24hours a day, in order to prevent any accident.
With security and safety at the forefront of our operations we have specially trained staff and fully-accredited processes to ensure the secure storage of dangerous goods. Alongside our warehouse capability we provide a full range of dangerous goods handling and transportation services. We can help you to find professional and cost effective solutions.
DG packing
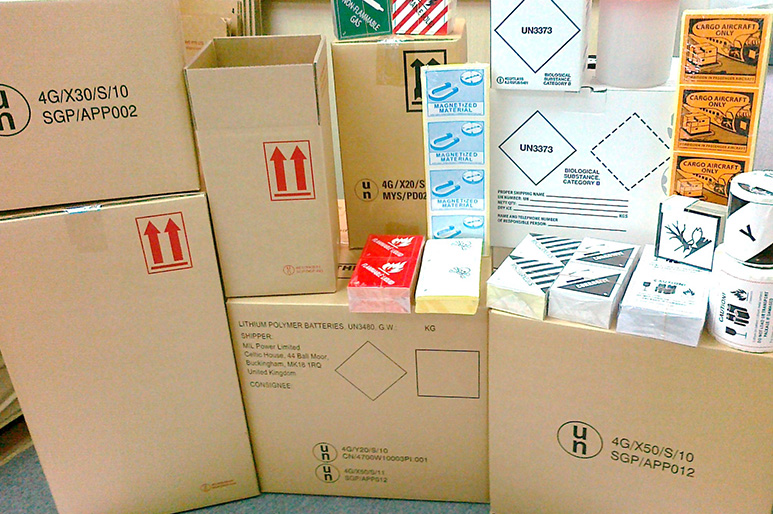

The dangerous goods package is very important in international transport. When established the information needed, you can then proceed to pack your goods in accordance to the regulations for the selected mode of transport; IATA/ICAO (Airfreight), IMDG (For Sea Freight), ADR (Road Freight)
The Information require to pack is; the UN number, proper shipping name, packing group (if applicable), shipper/consignee address, and a emergency contact number for manufacture of hazardous goods. Also Ideally need, a material safety data sheet (MSDS) for the product you are shipping. It will include the hazard details needed for transport. (section 14)
The packing work is necessary, to ensure that packaging conform to the standard of transportation safty.
DG Knowledge

The rules for classification are very widely defined, but some, for example most medicines and cosmetics, do not have the hazardous properties that would bring them within scope of the requirements, and those that do are usually carried in very small receptacles, allowing at least partial exemption from the requirements (either limited quantities or limited loads)
Consignors have a duty to identify the hazards of the goods they intend to transport. There are nine classes, some with divisions, as follows.
 Works through the categories in logical sequence. It sets out descriptions and criteria in some detail. The consignor must assign a "proper shipping name" and UN Number to the substance.
Works through the categories in logical sequence. It sets out descriptions and criteria in some detail. The consignor must assign a "proper shipping name" and UN Number to the substance.
All relevant hazards have to be determined. There is a hierarchy of classification and there are rules about choosing the most appropriate entry and hence UN number.
Once a UN number and proper shipping name have been assigned, some substances with the same name will have different degrees of danger (for example flash point). This is reflected in the “packing group” (PG), Where a substance has been classified from “first principles”, its PG will be determined by its properties.
Proper shipping names may also be qualified by the addition of the terms such as 'SOLUTION'; 'LIQUID'; 'SOLID'; 'MOLTEN', 'STABILIZED'.
Limited quantity (LQ) exemptions
From 2011. The limited quantity mark is:
or if an air mode journey is involved
Mark has to be minimum 100 mm x 100 mm unless package is too small.
In that case the minimum is 50 mm x 50 mm